Evaluasi Ergonomi pada Kursi Roda untuk Anak Cerebral Palsy Menggunakan Digital Human Modeling
Ergonomics Evaluation of Wheelchair for Children with Cerebral Palsy using Digital Human Modeling
Abstract views: 425 | pdf downloads: 437
Abstract
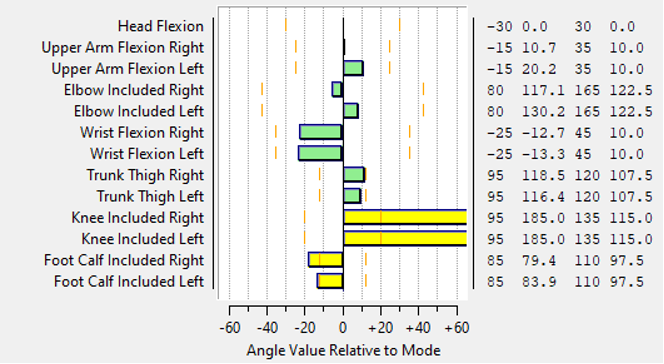
Cerebral palsy is caused by brain damage that manifests as motor dysfunction. The most prevalent form of cerebral palsy is spastic diplegia, which causes walking difficulties. People with cerebral palsy, particularly children, require mobility aids, such as wheelchairs, to perform daily tasks. When designing wheelchairs for children with cerebral palsy, ergonomic evaluation is required to ensure that the resulting wheelchair is safe and will not pose a risk in the future. This paper investigates the use of digital human modeling to evaluate the ergonomics of wheelchairs for children with cerebral palsy. The method is used to collect samples from 5 to 18-year-old children with cerebral palsy. Digital human modeling is used to simulate and evaluate ergonomics using anthropometric data. The results obtained for the wheelchair dimensions are suitable for the 95th percentile value, while the seat length exceeds the popliteal length for the 50th percentile value. The ergonomic evaluation yielded satisfactory results for the lower back analysis parameter, and the comfort evaluation yielded satisfactory results for the 95th percentile value. In contrast, the 5th percentile value indicates knee discomfort in both the right and left knee.
Downloads
References
Anwary, A.R. dkk. (2021) ‘Smart-Cover: A real time sitting posture monitoring system’, Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 317, hal. 1–16.
Ariffin, R.A. dkk. (2020) ‘An Ergonomic Perspective of User Need on Physio-Treadmill (PhyMill) Criteria: Knowledge and Awareness of Cerebral Palsy among Future Parents’, Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1529(5), hal. 052071.1-052071.8.
Arsyad, M. dan Anzarih, A.M. (2017) ‘Rancang Bangun Kursi Penderita Cereblal Palsy’, INTEK: Jurnal Penelitian, 4(2), hal. 103–106.
Eviani, D. (2019) Pentingnya Program Khusus Bina Diri Dan Bina Gerak Pada Anak Cerebral Palsy. Tugas Akhir. Program Studi Pendidikan Khusus Universitas Lambung Mangkurat.
Hu, J. dkk. (2022) ‘Construction of Evaluation Index System of Office Sitting Comfort Based on Ergonomics’, Modelling and Simulation in Engineering, 2022, hal. 1–12.
IEA, - International Ergonomic Association (2022) What Is Ergonomics (HFE)?, What Is Ergonomics (HFE)? Available at: https://iea.cc/about/what-is-ergonomics/ [Online] (Diakses: 1 November 2022).
Isharyadi, F. dan Ningtyas, D.R. (2013) ‘Kesesuaian SNI 12-0179-1987 Bagi Penderita Disabilitas di Indonesia’, Jurnal Standarisasi, 15(3), hal. 230–239.
Nabilah, N., Shanat, M. dan Mohamaddan, S. (2020) ‘An Anthropometric Measurement Of Cerebral Palsy Children For Developing Product Design’, International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research, 8, hal. 2708–2711.
Satheeshkumar, M. dan Krishnakumar, K. (2022) ‘Ergonomic Assessment of Lower Back Pain Among Coir Industry Workers and Workstation Modification’, Technology-Enabled Work-System Design, 2022, hal. 11–19.
Sun, Y. dkk. (2020) ‘Ergonomics Analysis of Hand-Held Grinding Operation Working Posture Based on Jack’, in S. Long and B.S. Dhillon (eds) Man–Machine–Environment System Engineering. Singapore: Springer (Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering), hal. 733–740.
Tanjung, A.S. dan Sinaga, N. (2022) Karakteristik Pasien Palsi Serebral Di Rumah Sakit Haji Medan tahun 2020-2021. Tugas Akhir. Fakultas Kedokteran, Universitas Muhammadiyah Sumatera Utara.
Wulandari, R., Weta, I.W. dan Imron, Moh.A. (2016) ‘Penambahan Latihan Hidroterapi Pada Terapi Bobath Lebih Meningkatkan Kecepatan Berjalan Pada Cerebral Palsy Spastik Diplegi’, Sport and Fitness Journal, 4(1), hal. 25–36.