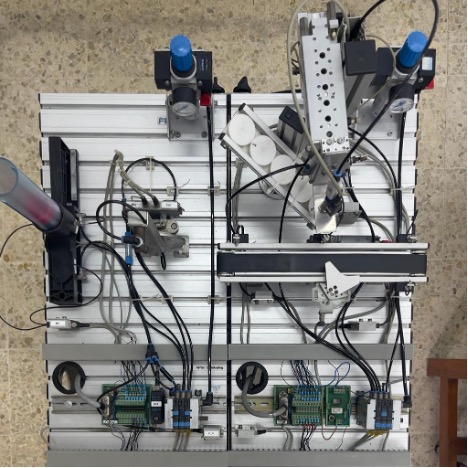
Design and Optimizing Top Cover Feeding Unit Modular Production System and Pick & Place Station
Abstract views: 100 | PDF downloads: 90
Abstract
Modular Production System is a station unit consisting of industrial components in the form of pneumatic and electrical components controlled by a Programmable Logic Controller which is directed for industry-oriented vocational training. In a Modular Production System, there are several types of stations, one of which is the pick and place station which consists of two modules, namely the pick and place module and the conveyor module. This design discusses the optimization of the design of the top cover feeding unit at the pick and place station because the top cover is dislocated every time there is a change in position when the vacuum sucks the top cover. This design optimization is done by redesigning the feeding unit slider. By doing this optimization, it can make the feeding unit accommodate the top cover where it should be and improve the process capability of the system. The results of this optimization are determined based on the process capability values, before optimization the resulting values were 1.0417 for Capabiity Process and 0.77 for the index. Then after design optimization, the values are 3.402 for Capabilty Process and 6.396 for the index and produce a total force of 0.205 N by using a slider feeding unit tilt angle of 14o. This tilt angle was determined as the most optimal angle because it resulted in the least system failure.
Downloads
References
Astro, R.B., Amirudin, D. and Mufida, D.H. (2017) ‘Analisis Koefisien Gesek Statis dan Kinetis Benda di Bidang Miring Menggunakan Video Tracker’, in Prosiding SKF 2017. Seminar Kontribusi Fisika (SKF 2017), Bandung, Indonesia: Program Studi Fisika Fakultas Matematika dan Ilmu Pengetahuan Alam Institut Teknologi Bandung, pp. 265–272.
Darto (2015) ‘Perencanaan Dan Simulasi Sistem Pneumatik Pada Mesin Pres Briket Blothong Berbantuan Perangkat Lunak’, Jurnal Teknologi dan Manajemen Informatika, 1(1), pp. 5–11.
FESTO (2023) Pick and Place Station, Festo Didactic InfoPortal. Available at: https://ip.festo-didactic.com/InfoPortal/MPS/PickandPlaceStation/EN/index.html (Accessed: 6 September 2023).
Hayati, N. and Hasanah, A.N. (2022) ‘Analisis Kapabilitas Proses Produksi Sediaan Drop dengan Menggunakan Program Statistik Minitab’, Majalah Farmasetika, 7(4), pp. 325–406.
Jenaro, A.D. and Suprianto, B. (2020) ‘Pengembangan Trainer MPS ( Modular Production System ) Pengisi Botol Air Otomatis Berbasis Mikrokontoler Arduino Mega Untuk Mata Pelajaran Pengendalian Sistem Robotik Di SMK Negeri 1 Jenangan’, Jurnal Pendidikan Teknik Elektro, 9(1), pp. 73–78.
Prastyo, A.U. et al. (2021) ‘Eksperimen Gaya Gesek Pada Bidang Miring Untuk Menguji Koefisien Gesek Statis Dan Kinetis’, Journal of Industrial Engineering UPY, 1(1), pp. 1–8.
Rahmawati, D. et al. (2020) ‘Analisis Kapabilitas Proses Pada Mesin Pengemasan Tepung Terigu PT. ISM Divisi Bogasari Flour Mills’, Teknoin, 26(1), pp. 1–13.
Ricky, M. and Habibullah, H. (2022) ‘Otomasi Penerangan Ruangan Berbasis Arduino Uno’, JTEIN: Jurnal Teknik Elektro Indonesia, 3(1), pp. 63–73.
Rimantho, D. and Athiyah, A. (2019) ‘Analisis Kapabilitas Proses Untuk Pengendalian Kualitas Air Limbah Di Industri Farmasi’, Jurnal Teknologi, 11(1), pp. 1–8.
Siva, F.A., Irawan, A.P. and Utama, D.W. (2023) ‘Design and Optimization of Modular Production System Distribution and Pick & Place Station’, International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology (IJISRT), 8(7), pp. 3057–3065.
Tanojo, D. (2015) ‘Kontrol Modular Production System Berbasis PLC Siemens S7-300 Dengan Menggunakan HMI Touch Panel Damaris Tanojo’, CALYPTRA, 4(1), pp. 1–8.
Taufiq (2017) Modular Production System (MPS) Stasiun Distribusi Dengan Siemens S7300. 1st edn. Jakarta, Indonesia: Direktorat Pembinaan Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan Kementerian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan. [Print].
Tuapetel, J.V. and Narwalutama, R. (2022) ‘Perencanaan Sistem Pneumatik Sebagai Penggerak pada Pintu Gerbong Kereta’, STRING (Satuan Tulisan Riset dan Inovasi Teknologi), 6(3), pp. 244–253.