Identifikasi dan Pengaruh Peubah Penekan dalam Peningkatan Performa Mesin Mobil
Identification and Effect of Suppressor Variable in Car Engine Performance Improvement
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.35814/asiimetrik.v5i1.4177Keywords:
engine, car engine performance, suppressor variableAbstract
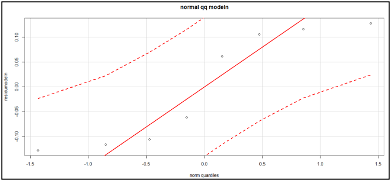
One of the manufacturing companies in the automotive industry produces motor vehicle components, including engines. Compared to other spare parts, the engine plays a crucial role in vehicle operation. The primary purpose of the engine is to generate rotary power through the combustion of the air and fuel mixture contained within it. Therefore, optimal engine performance must be considered for the perfection of motorized vehicles, and external supporting factors that contribute to optimal engine performance must be identified. If this external supporting factor correlates with the used variables, it can be identified as a suppressor variable. A suppressor variable can improve engine performance by increasing the value of the coefficient of determination. The objectives of this study are to determine the type of suppressor variable and whether the suppressor variable can affect the performance of a car engine. According to the findings of this study, tire size (positive net suppression) and digital tuning (negative classical suppression) are suppressor variables that can influence the enhancement of automobile engine performance
Downloads
References
Almanaf (2015) Analisa Kegagalan Produk Vulkanisir Ban. Skripsi. Program Studi Teknik Mesin S1, Fakultas Teknik, Universitas Riau.
Assauri, S. (1987) Manajemen Pemasaran : Dasar, Konsep, dan Strategi. 1st edn. Jakarta: Raja Grafindo Persada [Cetak].
Baguley, T. (2018) Serious Stat: A guide to advanced statistics for the behavioral sciences. 1st edn. London: Bloomsbury Publishing [Cetak].
Cohen, J. dkk. (2013) Applied Multiple Regression/Correlation Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. 3rd edn. New York: Routledge [Cetak].
Elsharif, T.A. (2019) ‘The Elements of Accounting Information Systems and the Impact of Their Use on the Relevance of Financial Information in Wahda Bank’, Open Journal of Business and Management, 7(3), hal. 1429–1450.
Friedman, L. dan Wall, M. (2005) ‘Graphical views of suppression and multicollinearity in multiple linear regression’, The American Statistician, 59(2), hal. 127–136.
Goldberg, L.R. (2013) Personality Topics in Honor of Jerry S. Wiggins: A Special Issue of Multivariate Behavioral Research. 1st edn. London: Psychology Press [Cetak].
Hendry, D.F. dan Morgan, M.S. (1997) The foundations of econometric analysis. 1st edn. Australia: Cambridge University Press [Cetak].
Horst, P. dkk. (1941) ‘The prediction of personal adjustment: A survey of logical problems and research techniques, with illustrative application to problems of vocational selection, school success, marriage, and crime’, Social Science Research Council, hal. 1–20.
Liu, H., Yuan, K.-H. dan Wen, Z. (2022) ‘Two-level moderated mediation models with single-level data and new measures of effect sizes’, Behavior Research Methods, 54(2), hal. 574–596.
Ludlow, L. dan Klein, K. (2014) ‘Suppressor variables: The difference between “is” versus “acting as”’, Journal of Statistics Education, 22(2), hal. 1–28.
Mohanty, S.S. (2014) ‘Suppressor Variable in Determining Targeted Catch of Exportable Marine Species in India’, Asian Journal of Research in Business Economics and Management, 4(4), hal. 77–88.
Ratmani, M. (2011) Buku Pengetahuan Ban Penumpang. 1st edn. Bekasi: PT. Multistrada Arah Sarana, Tbk. [Cetak].
Watson, D. dkk. (2013) ‘The Value of Suppressor Effects in Explicating the Construct Validity of Symptom Measures’, Psychological assessment, 25(3), hal. 929–941.