Exploratory Factor Analysis for Developing Wheelchairs for Children with Cerebral Palsy
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.35814/asiimetrik.v7i1.7769Keywords:
Wheel chairs, cerebral palsy, exploratory factor analysis, product designAbstract
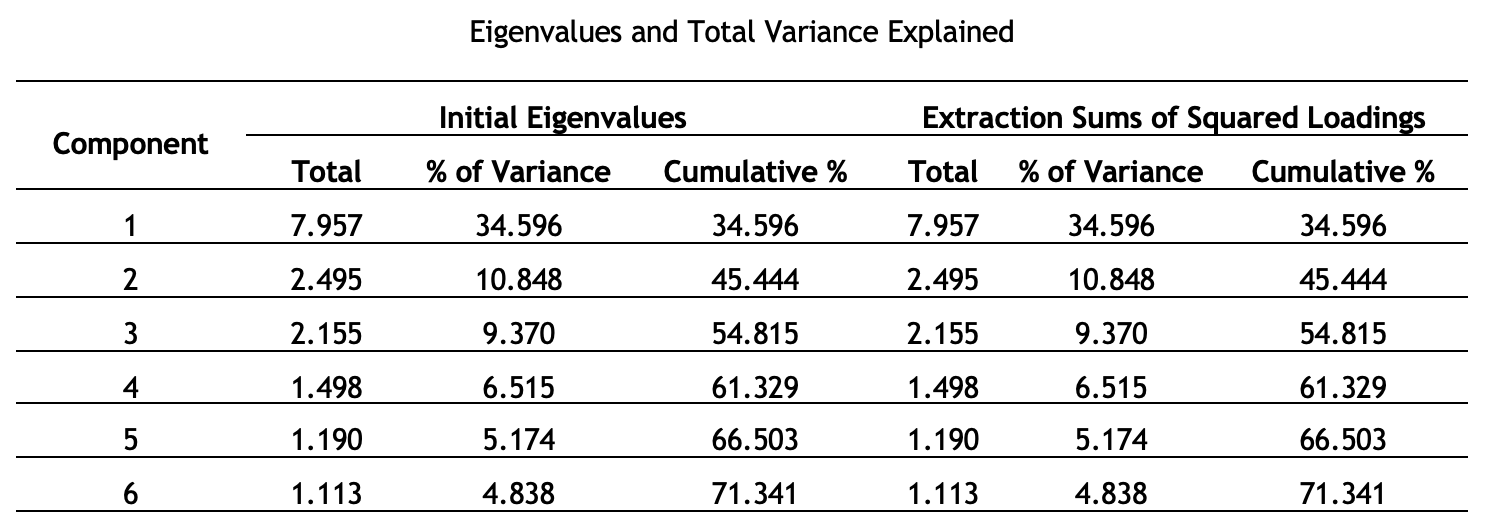
A wheelchair is an essential mobility tool for individuals with limitations, including children with Cerebral Palsy (CP). Cerebral palsy affects children under five and causes stiffness in various body parts. The design of wheelchairs for children with CP differs significantly from standard wheelchairs, prompting this research to identify the key factors that should be considered in designing such wheelchairs. This study used exploratory factor analysis, data was gathered from children with CP and their caregivers in Java. The findings revealed six fundamental factors to consider when designing wheelchairs for children with CP: Main features, Ultimate comfort, standard compliance, robust durability, thoughtful ergonomics, unique special features, user-friendly design, and aesthetic appeal. In summary, while the main features are crucial in the design of wheelchairs for children with CP, it is equally important that these wheelchairs comply with applicable standards and incorporate special features tailored specifically for these young users.
Downloads
References
Carlon, S.L. et al. (2013) ‘Differences In Habitual Physical Activity Levels Of Young People With Cerebral Palsy And Their Typically Developing Peers: A Systematic Review’, Disability and Rehabilitation, 35(8), pp. 647–655. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3109/09638288.2012.715721.
Ekiz, T. et al. (2017) ‘Wheelchair Appropriateness In Children With Cerebral Palsy: A Single Center Experience’, Journal of Back and Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation, 30(4), pp. 825–828. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3233/BMR-150522.
Goodlich, B.I. et al. (2020) ‘Machine Learning To Quantify Habitual Physical Activity In Children With Cerebral Palsy’, Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 62(9), pp. 1054–1060. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.14560.
Ho, M. et al. (2020) ‘The Process Of Designing Special Wheel Chair For People With Physical Disabilities’, Malaysian Journal of Public Health Medicine, 20(Special1), pp. 192–200. Available at: https://doi.org/10.37268/mjphm/vol.20/no.Special1/art.706.
Isharyadi, F. and Ningtyas, D.R. (2013) ‘Kesesuaian SNI 12-0179-1987 Bagi Penderita Disabilitas Di Indonesia’, Jurnal Standardisasi, 15(3), pp. 230–239. Available at: https://doi.org/10.31153/js.v15i3.126.
Kharisma, A. and Indrojarwo, B.T. (2017) ‘Desain Kursi Roda dengan Sistem Kemudi Tuas sebagai Sarana Mobilitas bagi Anak Penderita Cerebral Palsy Usia 6 hingga 10th’, Jurnal Sains dan Seni ITS, 5(2), pp. 271–275. Available at: https://doi.org/10.12962/j23373520.v5i2.21007.
Levitt, S. and Addison, A. (2018) Treatment of Cerebral Palsy and Motor Delay. John Wiley & Sons. [Print].
Llontop, D.A.R. et al. (2020) ‘Mechatronics Design and Simulation of Anthropomorphic Robotic Arm mounted on Wheelchair for Supporting Patients with Spastic Cerebral Palsy’, in 2020 IEEE International Conference on Engineering Veracruz (ICEV). 2020 IEEE International Conference on Engineering Veracruz (ICEV), Boca del Rio, Mexico: IEEE, pp. 1–5. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEV50249.2020.9289665.
Maher, C.A. et al. (2007) ‘Physical and sedentary activity in adolescents with cerebral palsy’, Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 49(6), pp. 450–457. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2007.00450.x.
Malik, F., Kamran, S. and Sarfraz, S. (2022) ‘Exploratory Factor Analysis of Internal Resource Based View for New Product Development Process in Pakistan’S Manufacturing Sector’’, Pakistan Journal of Social Research, 4(2), pp. 222–233. Available at: https://doi.org/10.52567/pjsr.v4i2.470.
Mardiana, D.P., Pujianto, M.R. and Sulistyo, S. (2020) ‘Perancangan Kursi Roda Ergonomis Untuk Orang Manula’, Journal of Industrial Engineering and Technology, 1(1), pp. 11–17. Available at: https://doi.org/10.24176/jointtech.v1i1.5618.
Mboi, N. (2014) ‘Peraturan Menteri Kesehatan Nomor 25 Tahun 2014 tentang Upaya Kesehatan Anak’. Permenkes. Available at: https://peraturan.bpk.go.id/Details/117562/permenkes-no-25-tahun-2014 (Accessed: 19 December 2024).
McNeish, D. (2017) ‘Exploratory Factor Analysis With Small Samples and Missing Data’, Journal of Personality Assessment, 99(6), pp. 637–652. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1080/00223891.2016.1252382.
Ordóñez, B.Q. et al. (2021) ‘Application of Exploratory Factor Analysis in the Construction of a Self-Perception Model of Informational Competences in Higher Education’, Mathematics, 9(18), p. 2332. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3390/math9182332.
Pradita, A.A., Priadythama, I. and Susmartini, S. (2018) ‘Perancangan Ulang Kursi Roda Manual Menggunakan Kriteria Standar ISO 7176-5’, Performa: Media Ilmiah Teknik Industri, 17(1), pp. 54–60. Available at: https://doi.org/10.20961/performa.17.1.19068.
Pratiwi, R.A. et al. (2019) ‘Usulan Kerangka Standar Kursi Roda Manual Sebagai Acuan Penyusunan Standar Nasional Indonesia (SNI)’, Jurnal Standardisasi, 20(3), pp. 207–217. Available at: https://doi.org/10.31153/js.v20i3.724.
Rodby-Bousquet, E. et al. (2016) ‘Physical risk factors influencing wheeled mobility in children with cerebral palsy: a cross-sectional study’, BMC pediatrics, 16(1), p. 165. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-016-0707-6.
Tanjung, A.S. and Sinaga, N. (2022) ‘Karakteristik Pasien Palsi Serebral Di Rumah Sakit Haji Medan tahun 2020-2021’, JURNAL ILMIAH SIMANTEK, 6(4), pp. 79–88.
Yong, A.G. and Pearce, S. (2013) ‘A Beginner’s Guide to Factor Analysis: Focusing on Exploratory Factor Analysis’, Tutorials in Quantitative Methods for Psychology, 9(2), pp. 79–94. Available at: https://doi.org/10.20982/tqmp.09.2.p079.
Zakiyah, U.M., Setiawan, R. and Rosnawati, R. (2022) ‘Exploratory Factor Analysis: Factors that Affects Parents’ Decision to Choose Private Elementary Schools in Pandemic Covid19’, in. Annual Conference on Research, Educational Implementation, Social Studies and History (AREISSH 2021), Yogyakarta, Indonesia: Atlantis Press, pp. 237–248. Available at: https://doi.org/10.2991/978-2-494069-17-6_26.
Zupan, A. and Jenko, M. (2012) ‘Assistive technology for people with cerebral palsy’, Eastern Journal Of Medicine, 17(4), pp. 194–197.